Share
- Details
-
The working principle of the electromagnetic power-off brake: the braking and separation of the power shaft are controlled by direct current, and the power-off brake is separated by power. However, when choosing products, one must not be greedy for petty gain, but should buy them from companies with complete strength and qualifications, because the reasonable optimization of the circuit of electromagnetic brake can ensure the safety and reliability of lifting, avoid jamming and other situations, and small workshops are likely to fail to guarantee the quality for the sake of efficiency. At the same time, because high-frequency operation will affect the life of components, professional and technical personnel usually have to regularly test them.
Electromagnetic power-loss brake is widely used in various lifting device operations, which not only greatly improves the efficiency of the operation, but also greatly reduces the labor cost and ensures the safety of the operation. Electromagnetic power-off brake has the advantages of low noise, low heat, high safety, quick braking time and excellent torque retention utility, etc. It has been widely used in lifting devices in various industries, especially in high-frequency braking occasions.
Electromagnetic power-off brake (power-off brake) has the advantages of compact structure, convenient installation, wide adaptability, low noise, high working frequency, sensitive action, and reliable braking. It is an ideal automatic actuator. It is widely used in metallurgy, construction, chemical industry, food, machine tools, printing, packaging and other mechanical equipment, and in the event of power failure (risk prevention) braking and other occasions.Electromagnetic power-off brake (power-off brake) uses and applications: suitable for metallurgy, machine tools, packaging, construction, chemical, food, stage, elevators, ships and other machinery and in the power-off (anti-risk) braking and other occasions, to achieve fast parking, accurate positioning, safety braking and other purposes.
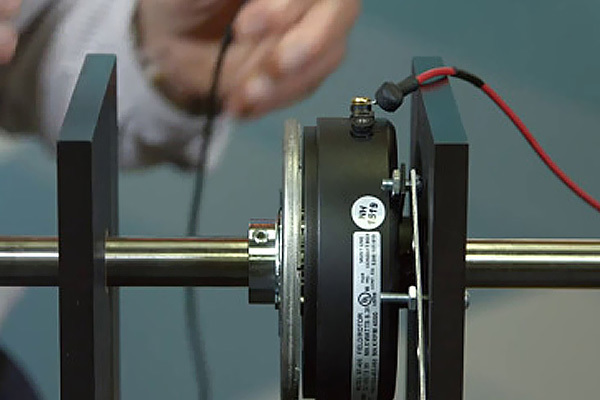
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The starting process of the motor will undergo a state transition from static to dynamic; after the motor is powered off during operation, it will undergo a transition from dynamic to static due to inertia. Most equipment has no requirement for the length of time from moving to static, but some equipment such as elevators, cranes, automated production lines, etc. must be stopped within a very short period of time after power failure, which introduces our topic today, motor brake control. The electromagnetic brake is generally installed at the non-shaft extension end of the motor. The motor shaft and the spline (external spline) are connected through an ordinary flat key, and then connected to the brake disc through a spline sleeve (external spline). When the motor is energized, the excitation coil of the brake is synchronously connected to the power supply. Under the action of electromagnetic force, the yoke attracts the armature to separate the armature from the brake disc, releasing the motor shaft, and the motor shaft with the brake disc runs normally or starts; When the power is off, the excitation coil loses power, and the electromagnetic force of the yoke attracting the armature disappears. The return spring pushes the brake disc and the armature to separate, forcing the brake disc and motor flange to generate friction torque, quickly stop the motor shaft.
In this particular emphasis:
(1) most of the loss of power brake is the use of DC voltage, that is, DC voltage. For the loss of power brakes used on AC motors, an AC to DC voltage converter is often required.
(2) In order to ensure the synchronization of the electromagnetic power loss brake and the power supply and power failure of the motor, the power supply line of the brake should be connected with the power supply line of the motor, and the connection should be reliable enough;
(3) The electromagnetic power loss brake can only ensure the timely release of the motor shaft when the voltage reaches or approaches the rated voltage. Therefore, this type of motor can not be started by step-down, otherwise it will cause the motor to block heat and burn the winding due to the stagnation of the motor rotor or the braking effect of the brake;
(4) The braking of the electromagnetic power-off brake is achieved by friction deceleration and spline engagement. Therefore, the gap between the stationary disc and the moving disc is very important. On the one hand, it is necessary to ensure the normal operation of the motor after the rotating shaft is released. On the other hand, it is necessary to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the braking action. In general, the gap has been adjusted in place according to the rated voltage of the matching motor when the brake leaves the factory, but when the brake is installed, the gap between the two discs should still be checked, including the check of the gap size and uniformity.
(5) For the short-circuit test of the motor, in view of the test procedure that the applied voltage is less than the rated voltage of the motor, the rotor of the motor does not need to be blocked during the short-circuit test, and the brake itself is a ready-made brake; However, when the motor is started, full pressure must be applied, and
Main performance parameters
Main Technical DataSpecifications
SizeRated transmission torque
Rated Static Torque
N.MRated voltage
Rated Voltage
D.C.VCoil power consumption (20 ℃)
Coil Consumption power(20℃)Maximum allowable speed
Allowed
Max Revolution
r/min4H4020753 3000 8H8020779 3000 15H 150 207 81 2500 30H300207114 2500 60H
600
207
145
2000
100H 1000 207 185 2000 160H 1600 207 220 1700 250H 2500 207 260 1500 Note: If the rated working voltage is different from the above table, it can be specially ordered by the user. For specifications above 100H, it is recommended to stop before braking.
Outline and installation dimensions
Overall and Installation Dimensions
Specifications Model
4H
8H
15H
30H
60H
100H
160H
250H
Radial dimension
D1
175
195
230
320
337
400
455
510
D2
150
170
202
280
300
375
430
480
D3
60
65
75
120
125
160
200
255
D4
70
72
85
120
125
145
180
215
D5
120
120
120
200
180
280
240
390
D6
—
—
—
—
—
175
—
260
D7
—
—
—
—
—
310
340
430
Axial dimension
L
73
80
104.6
127
163.8
168
183
191
L1
15
15
15
20
28
20
20
30
L2
30
30
35
50
56
75
125
130
L3
4
4
4
4
4
—
—
—
L4
—
—
—
—
—
5
5
5
Δ
0.4
0.5
0.5
0.6
0.8
1
1
1
Shaft hole size
Φ
29.5
39.5
44.5
59
65
80
95
85
e
8
12
12
18
18
22
25
22
h
32.8
42.8
47.8
63.4
69.4
85.4
100.4
90.4
Other dimensions
Α
30°
37.5°
47.5°
15°
75°
11.25°
11.25°
11.25°
M1
3 × M6
3 × M8
4 × M10
4 × M12
6 × M12
8 × M12
8 × M12
8 × M16
M2
3 × M6
3 × M8
4 × M8
4 × M12
4 × M12
—
—
—
M3
2 × M5
2 × M5
2 × M5
2 × M5
4 × M5
4 × M6
4 × M5
4 × M6
P
200
200
500
350
500
500
500
500
DHM3-H type electromagnetic power-off brake
Classification
Keyword
Electromagnetic power-loss clutch
- Details
-
The working principle of the electromagnetic power-off brake: the braking and separation of the power shaft are controlled by direct current, and the power-off brake is separated by power. However, when choosing products, one must not be greedy for petty gain, but should buy them from companies with complete strength and qualifications, because the reasonable optimization of the circuit of electromagnetic brake can ensure the safety and reliability of lifting, avoid jamming and other situations, and small workshops are likely to fail to guarantee the quality for the sake of efficiency. At the same time, because high-frequency operation will affect the life of components, professional and technical personnel usually have to regularly test them.
Electromagnetic power-loss brake is widely used in various lifting device operations, which not only greatly improves the efficiency of the operation, but also greatly reduces the labor cost and ensures the safety of the operation. Electromagnetic power-off brake has the advantages of low noise, low heat, high safety, quick braking time and excellent torque retention utility, etc. It has been widely used in lifting devices in various industries, especially in high-frequency braking occasions.
Electromagnetic power-off brake (power-off brake) has the advantages of compact structure, convenient installation, wide adaptability, low noise, high working frequency, sensitive action, and reliable braking. It is an ideal automatic actuator. It is widely used in metallurgy, construction, chemical industry, food, machine tools, printing, packaging and other mechanical equipment, and in the event of power failure (risk prevention) braking and other occasions.Electromagnetic power-off brake (power-off brake) uses and applications: suitable for metallurgy, machine tools, packaging, construction, chemical, food, stage, elevators, ships and other machinery and in the power-off (anti-risk) braking and other occasions, to achieve fast parking, accurate positioning, safety braking and other purposes.
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The starting process of the motor will undergo a state transition from static to dynamic; after the motor is powered off during operation, it will undergo a transition from dynamic to static due to inertia. Most equipment has no requirement for the length of time from moving to static, but some equipment such as elevators, cranes, automated production lines, etc. must be stopped within a very short period of time after power failure, which introduces our topic today, motor brake control. The electromagnetic brake is generally installed at the non-shaft extension end of the motor. The motor shaft and the spline (external spline) are connected through an ordinary flat key, and then connected to the brake disc through a spline sleeve (external spline). When the motor is energized, the excitation coil of the brake is synchronously connected to the power supply. Under the action of electromagnetic force, the yoke attracts the armature to separate the armature from the brake disc, releasing the motor shaft, and the motor shaft with the brake disc runs normally or starts; When the power is off, the excitation coil loses power, and the electromagnetic force of the yoke attracting the armature disappears. The return spring pushes the brake disc and the armature to separate, forcing the brake disc and motor flange to generate friction torque, quickly stop the motor shaft.
In this particular emphasis:
(1) most of the loss of power brake is the use of DC voltage, that is, DC voltage. For the loss of power brakes used on AC motors, an AC to DC voltage converter is often required.
(2) In order to ensure the synchronization of the electromagnetic power loss brake and the power supply and power failure of the motor, the power supply line of the brake should be connected with the power supply line of the motor, and the connection should be reliable enough;
(3) The electromagnetic power loss brake can only ensure the timely release of the motor shaft when the voltage reaches or approaches the rated voltage. Therefore, this type of motor can not be started by step-down, otherwise it will cause the motor to block heat and burn the winding due to the stagnation of the motor rotor or the braking effect of the brake;
(4) The braking of the electromagnetic power-off brake is achieved by friction deceleration and spline engagement. Therefore, the gap between the stationary disc and the moving disc is very important. On the one hand, it is necessary to ensure the normal operation of the motor after the rotating shaft is released. On the other hand, it is necessary to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the braking action. In general, the gap has been adjusted in place according to the rated voltage of the matching motor when the brake leaves the factory, but when the brake is installed, the gap between the two discs should still be checked, including the check of the gap size and uniformity.
(5) For the short-circuit test of the motor, in view of the test procedure that the applied voltage is less than the rated voltage of the motor, the rotor of the motor does not need to be blocked during the short-circuit test, and the brake itself is a ready-made brake; However, when the motor is started, full pressure must be applied, and
Main performance parameters
Main Technical DataSpecifications
SizeRated transmission torque
Rated Static Torque
N.MRated voltage
Rated Voltage
D.C.VCoil power consumption (20 ℃)
Coil Consumption power(20℃)Maximum allowable speed
Allowed
Max Revolution
r/min4H4020753 3000 8H8020779 3000 15H 150 207 81 2500 30H300207114 2500 60H
600
207
145
2000
100H 1000 207 185 2000 160H 1600 207 220 1700 250H 2500 207 260 1500 Note: If the rated working voltage is different from the above table, it can be specially ordered by the user. For specifications above 100H, it is recommended to stop before braking.
Outline and installation dimensions
Overall and Installation Dimensions
Specifications Model
4H
8H
15H
30H
60H
100H
160H
250H
Radial dimension
D1
175
195
230
320
337
400
455
510
D2
150
170
202
280
300
375
430
480
D3
60
65
75
120
125
160
200
255
D4
70
72
85
120
125
145
180
215
D5
120
120
120
200
180
280
240
390
D6
—
—
—
—
—
175
—
260
D7
—
—
—
—
—
310
340
430
Axial dimension
L
73
80
104.6
127
163.8
168
183
191
L1
15
15
15
20
28
20
20
30
L2
30
30
35
50
56
75
125
130
L3
4
4
4
4
4
—
—
—
L4
—
—
—
—
—
5
5
5
Δ
0.4
0.5
0.5
0.6
0.8
1
1
1
Shaft hole size
Φ
29.5
39.5
44.5
59
65
80
95
85
e
8
12
12
18
18
22
25
22
h
32.8
42.8
47.8
63.4
69.4
85.4
100.4
90.4
Other dimensions
Α
30°
37.5°
47.5°
15°
75°
11.25°
11.25°
11.25°
M1
3 × M6
3 × M8
4 × M10
4 × M12
6 × M12
8 × M12
8 × M12
8 × M16
M2
3 × M6
3 × M8
4 × M8
4 × M12
4 × M12
—
—
—
M3
2 × M5
2 × M5
2 × M5
2 × M5
4 × M5
4 × M6
4 × M5
4 × M6
P
200
200
500
350
500
500
500
500
Product inquiry

The company has a product research and development department composed of experts, senior engineers and other professional and technical personnel. It is engaged in research and development and has perfect research and development test equipment. At present, the products reach more than 100 series of nearly 1,000 specifications, and the force distance ranges from 0.1N. m ~ 250000N.m. The company has been rated as a high-tech enterprise by the state for more than ten consecutive years, and a number of R & D projects have been established locally and have received municipal financial support.
Service Hotline:
Sales Department: Xu Jie
Sales Phone:+86-22-26616372, +86-22-26341260, +86 13920613215
Fax: 86-022-26616580
Market Development Department: Li Shuo
Marketing Department Telephone:+86-22-26614130
Technology Department: Yue Chao
Technical Department Telephone:+86-22-26222775 ,+86 18602228435
QQ:1059237223 1611412939
Company Website:www.tjlhq.com
Enterprise E-mail:xzm@tjlhq.com
Company address: No.6, Zone B, South Jifeng Road, Hongcang City Industrial Park, Yanji Daohong, Beichen District, Tianjin